Imagine stepping into a world where surgeons don’t just wield scalpels but also wear VR headsets. Welcome to the fascinating realm of virtual reality in medicine and surgery, where technology meets life-saving precision. This isn’t just a sci-fi fantasy; it’s transforming how doctors train, plan, and perform procedures.
With VR, medical professionals can practice complex surgeries in a risk-free environment, perfecting their skills without the pressure of a real operating room. It’s like playing a video game, but instead of saving princesses, they’re saving lives. As this innovative tool continues to evolve, it promises to revolutionize patient care and enhance surgical outcomes, proving that the future of medicine is not only bright but also a little bit fun.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Virtual Reality in Medicine and Surgery
Virtual reality (VR) revolutionizes the way medicine and surgery are practiced. This technology immerses users in a simulated environment, offering a unique platform for training and procedural rehearsals. Medical professionals often use VR to refine their skills without the risk associated with real-life surgeries.
Simulation-based training programs utilize VR to enable learners to engage in various surgical scenarios. During these simulations, users encounter realistic surgical situations that enhance decision-making and technical proficiencies. Practicing in a virtual realm leads to increased confidence, which directly translates to improved performance in actual operating rooms.
Patient education also benefits from VR. Individuals receive detailed visualizations of procedures, making complex medical concepts more accessible. Understanding surgical processes reduces anxiety and fosters trust between patients and medical teams.
Research supports that integrating VR into medical education enhances knowledge retention. Studies show that learners retain information better when they engage in immersive training rather than traditional methods. The enhanced engagement contributes to a more effective education model.
VR isn’t limited to training; it also offers therapeutic applications. Therapists can use VR to treat conditions such as phobias and post-traumatic stress disorder by simulating exposure to patients’ fears. This innovative method enhances the therapeutic process and promotes recovery.
The future of virtual reality in medicine looks promising. Continuous advancements in technology indicate that VR will play an increasingly significant role in training and patient care. As the healthcare landscape evolves, embracing VR paves the way for improved surgical techniques and overall health outcomes.
Applications of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
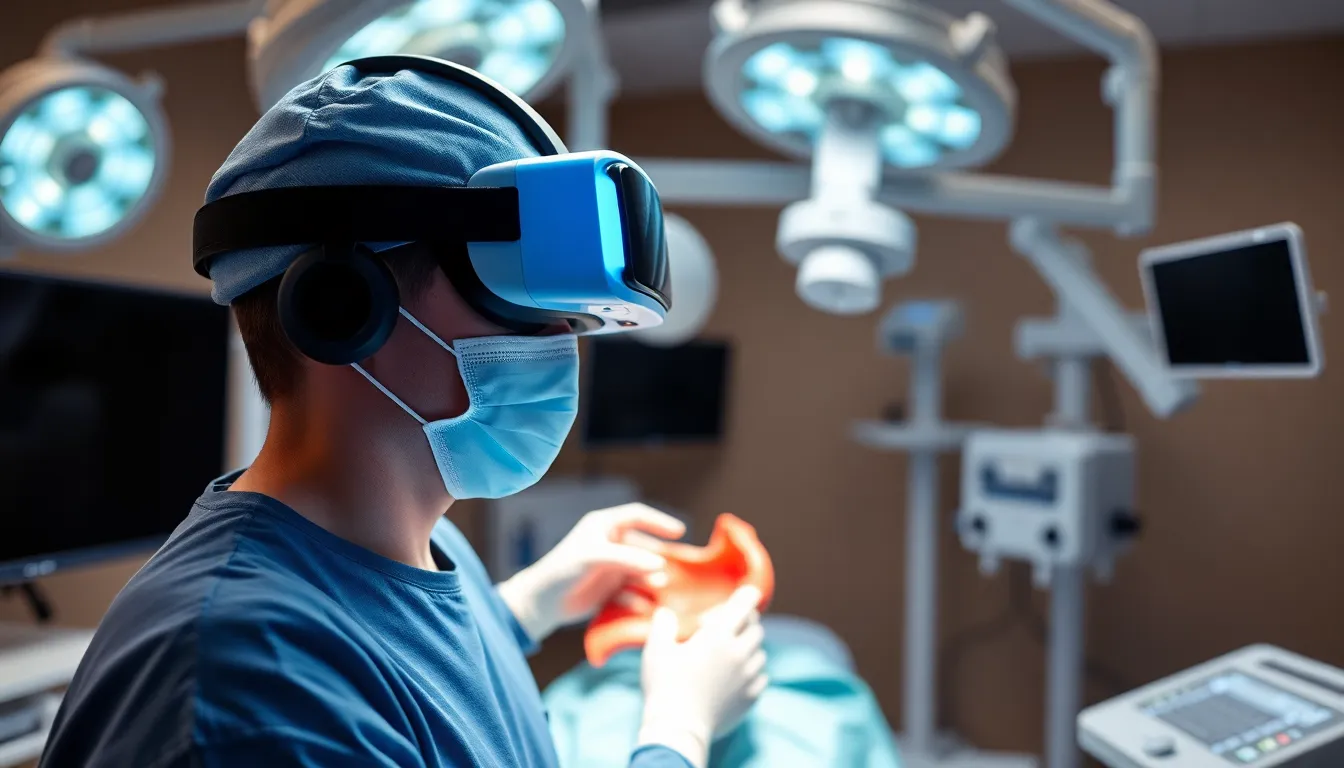
Virtual reality enhances medical training through immersive simulations, improving skills and knowledge retention.
Simulation for Surgical Procedures
Surgeons benefit from VR simulations that mirror real-life scenarios. These simulations allow for repeated practice of complex techniques without the risks associated with live procedures. Participants engage in various surgical cases, refining their decision-making abilities while encountering diverse challenges. Research demonstrates that this hands-on experience through VR significantly boosts surgical proficiency. Additionally, feedback in simulated environments helps them correct mistakes in real-time, solidifying learning. The ability to practice anywhere also increases access for training opportunities, bringing advanced skills to medical professionals without geographical limitations.
Enhancing Patient Interactions
Engaging patients through VR creates unique educational opportunities. Detailed simulations of surgical procedures provide visual context, aiding in understanding complex information. This approach reduces patient anxiety by allowing them to visualize what to expect before surgery. Trust between patients and medical teams flourishes as patients experience procedures in a safe, interactive environment. Moreover, VR tools empower healthcare providers to convey information more effectively, fostering better communication and clearer expectations. Overall, these interactions promote patient comfort and confidence, leading to improved satisfaction in care.
Benefits of Virtual Reality in Surgical Environments
Virtual reality significantly enhances surgical environments, offering numerous advantages for medical professionals and patients alike.
Improved Surgical Precision
Precision in surgery receives a substantial boost from VR technology. Surgeons access realistic simulations that replicate the intricacies of actual procedures. Practice in these environments allows for refining techniques without the risks tied to live surgeries. Mistakes during training get corrected in real-time, offering immediate feedback. Enhanced spatial awareness results from navigating virtual spaces, translating to improved accuracy during actual operations. Studies show that surgeons who utilize VR components often exhibit better outcomes in high-stakes situations. As skills develop, confidence level rises, leading to a more steady hand during critical moments.
Reduced Training Costs
Surgical training expenses decrease significantly with the use of VR. Traditional training methods often incur high costs related to equipment, facilities, and learning materials. By incorporating VR simulations, medical institutions cut down on these expenses while maintaining high training standards. Access to VR platforms allows greater participation, eliminating geographical barriers for trainees. Moreover, augmented training opportunities lead to faster learning, which can reduce the total time spent in training. Institutions benefit from efficiently training more staff without the additional financial burden. This efficiency not only optimizes resources but also enhances the overall quality of surgical education.
Challenges and Limitations
Virtual reality (VR) in medicine and surgery presents several challenges and limitations that require attention. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for maximizing VR’s potential in healthcare.
Technological Barriers
Technological limitations pose significant challenges for implementing VR in medical practice. High costs associated with VR hardware and software often restrict access. Complexity in integration into existing medical systems can create hurdles for healthcare facilities. Additionally, variability in the quality of VR simulations affects user experience and effectiveness in training. Developers must ensure that these simulations accurately represent real-life procedures to provide meaningful training. Performance issues, including latency and user discomfort, can further hinder adoption. As these technological barriers are addressed, more healthcare providers could embrace VR as a valuable training tool.
Acceptance Among Medical Professionals
Acceptance of VR among medical professionals varies widely. Some healthcare practitioners express skepticism regarding its effectiveness compared to traditional training methods. Concerns about the practicality of VR in real-world applications also exist. Ensuring that VR technology aligns with clinical needs is essential for gaining trust. Educational initiatives highlighting successful case studies can encourage wider adoption among practitioners. Peer influence plays a crucial role in shaping perceptions, with early adopters often fostering interest within their institutions. Greater exposure to VR training programs can gradually increase acceptance and integrate this innovative method into standard practices.
Future Trends in Virtual Reality
Virtual reality in medicine is rapidly evolving, with many exciting developments on the horizon. Enhanced simulations likely drive improvements in surgical training, leading to even more realistic experiences for medical professionals.
Innovations on the Horizon
New advancements in VR technology focus on improved hardware and software, which will enhance user experience and realism in simulations. Higher resolution graphics and advanced haptic feedback generate immersive environments that mimic real-life situations even more closely. Further developments include AI integration, allowing simulations to adapt dynamically based on user performance. These innovations predict a future where surgeons train in virtual environments that replicate various scenarios, improving competencies across various specializations. Research supports that these advancements can lead to quicker learning curves and superior competency in actual procedures.
Integration with Other Technologies
Combining VR with augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) creates a powerful tool for medical applications. AR overlays essential information directly onto the surgeon’s field of vision, while AI analyzes user actions and offers real-time feedback. This integration allows medical professionals to make informed decisions during surgeries, enhancing precision and outcomes. Moreover, utilization of VR in telemedicine could revolutionize remote consultations, providing immersive experiences for patients. By linking these technologies, healthcare providers create a comprehensive, interactive training and patient care platform, bolstering effectiveness and efficiency in medical practice.
The integration of virtual reality in medicine and surgery is reshaping the landscape of medical training and patient care. As VR technology continues to evolve it promises to enhance surgical precision and improve educational outcomes for medical professionals. The immersive training experiences foster confidence and skill development while also facilitating better communication between healthcare providers and patients.
Despite existing challenges the future of VR in healthcare looks bright. Ongoing advancements in technology will likely address current limitations and expand the applications of VR in both training and therapeutic settings. Embracing these innovations can lead to improved surgical techniques and overall health outcomes, making virtual reality an invaluable asset in the medical field.


